Your Cart
Sub Heading
Product Carousel
Use this text to share the information which you like!.
Here are two examples:
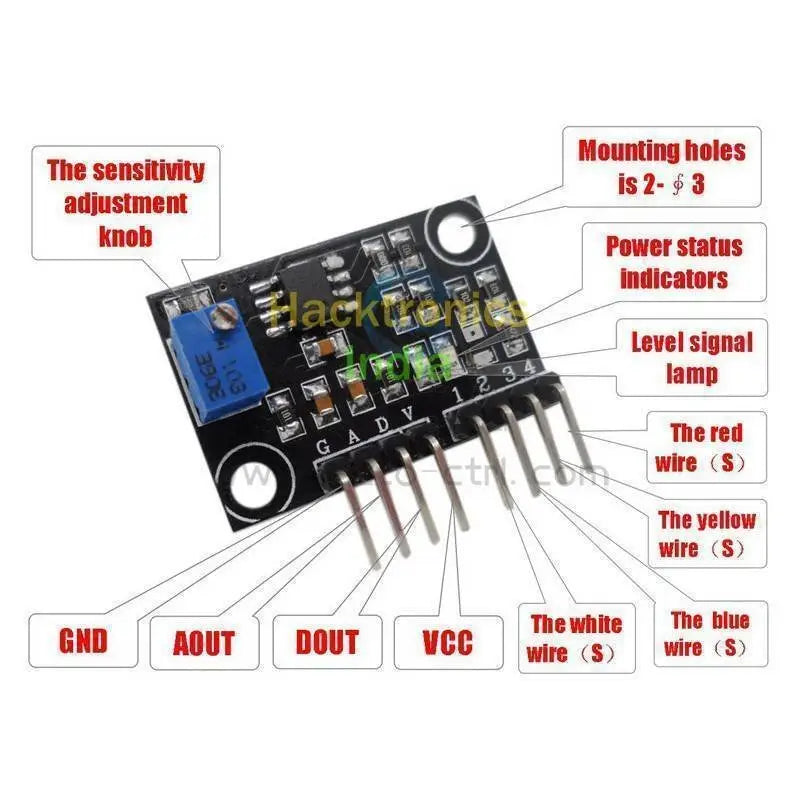
Example 1 uses Analog output mode
Example 2 uses Digital output mode
void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); //Baud rate: 9600 } void loop() { int sensorValue = analogRead(A0); // read the input on analog pin 0: float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1024.0); // Convert the analog reading (which goes from 0 - 1023) to a voltage (0 - 5V): Serial.println(voltage); // print out the value you read: delay(500); }
int ledPin = 13; // Connect an LED on pin 13, or use the onboard one int sensor_in = 2; // Connect turbidity sensor to Digital Pin 2
void setup(){ pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set ledPin to output mode pinMode(sensor_in, INPUT); //Set the turbidity sensor pin to input mode }
void loop(){ if(digitalRead(sensor_in)==LOW){ //read sensor signal digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // if sensor is LOW, then turn on }else{ digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // if sensor is HIGH, then turn off the led } }
This is a reference chart for the mapping from the output voltage to the NTU according to different temperature. e.g. If you leave the sensor in the pure water, that is NTU < 0.5, it should output “4.1±0.3V” when temperature is 10~50℃.
characteristic curve “Voltage ----Temperature
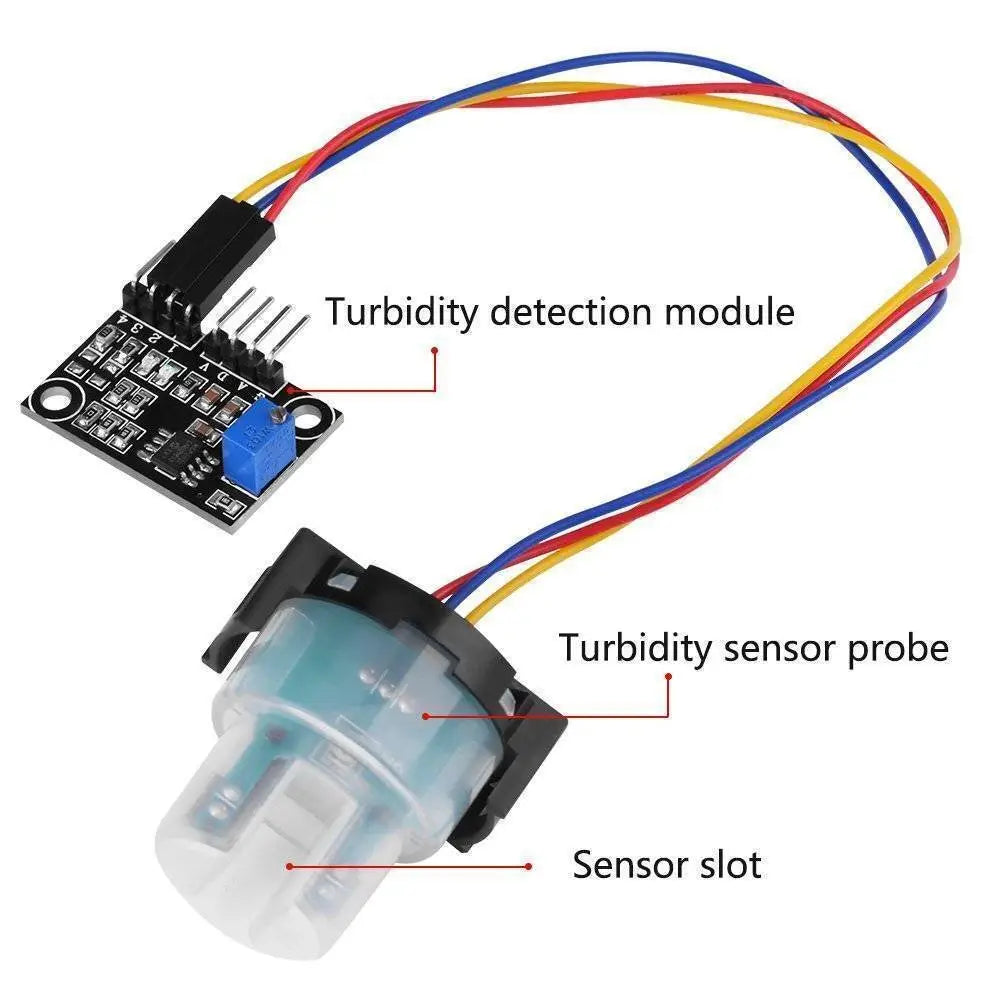

Use this text to share the information which you like!.
Recently viewed!